Many readers are interested in the appropriate subject: athlete’s feet (Tinea Pedis). Our makers are pleased to report that they have already done modern research studies on the subject you are fascinated by. We will give you a wide range of answers based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample survey information. Keep repeating to verify the details.
The characteristic results that occur with medical demonstrations are sufficient to make a foot diagnosis in a suspect athlete. The treating physician has the option of ordering a skin analysis for microscopic examination anyway.
Athlete’s foot: what is it and how can it be prevented?
Fungal Infection of the Athlete’s Foot or Pedi or Foot (Athlete’s Foot)
Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection of the foot that occurs in men, women and boys of all ages. It is not limited to athletes For example, the area is it as athletes generally sweat. Additionally, they wear tight-fitting shoes. This makes their feet sensitive to wet conditions on the inside of the shoe. As a result, they are more susceptible to the development of fungal infections. Fungal arguments are present in the areas around us. These arguments germinate and fungal outbreaks occur when they find favorable wet and humid conditions. They are composed of small wire-shaped fungal threads. Countless fungal threads join together into mycelia.
The athlete Feet are considered a form of superficial fungal infection named dermatomycosis (dermal skin, plant growth) and are usually confined to the epidermis and dermis. They feed on keratin proteins in the nails (tinea unguis), skin (named after their role in the body), and hair. They usually cause itching on the sports (gro caliber, also known as Tinea cruris), scalp (Tinea capitis) or general (on the fur on the hull).
Athletes foot: how does it occur?
This situation includes certain predisposing factors that make some people more vulnerable to infection. There are immunodeficiency disorders and debilitating disorders (usually idiopathic) such as sweet diabetes and palm or plantar enlargement. In addition, there are poor hygiene practices, such as not changing socks (in the case of athlete’s foot) or undergarments (in other cases of dermatofecal disease). Athlete’s foot is contagious (due to direct contact). Shoes that are soiled with the joint introduction of their own clean towels may spread the disease among healthy persons. Walking barefoot in social spaces such as swimming pools, showers, gyms and other changing rooms is still considered a documented risk.
athlete ’s foot symptoms
People with athlete’s feet tend to feel better:
- Painful blisters between fingers and toes.
- Mild itchy or burning rash. May swear by bloody or serous discharge or bleed.
- Dry soles and feet with great chance of rupturing and bursting.
- Thick, discolored nails that can crumble and simply peel off.
- Complications include distribution to other areas (by repeatedly scratching the infected area), e.g. gro radius (Tinea cruris). There is also the possibility of spread to the nails. This causes shingles and weak adhesion to the nail bed. People with diabetes or on immunosuppressive drugs may still acquire nontreatable ulcers.
Diagnosis of athlete’s foot
The characteristic results that occur with medical demonstrations are sufficient to make a foot diagnosis in a suspect athlete. The treating physician has the option of ordering a skin analysis for microscopic examination anyway.
Skin scrapings are examined with 10% KOH (potassium hydroxide). This will color the fungal mycelium but will not affect the epidermal cells of the skin.
athlete ’s foot treatment
Most importantly, foot hygiene should be observed.
It is helpful to wear soft, preferably cotton socks and change them daily. Ignore dense shoes from rubber/vinyl that are on the feet. This is because this leads to heat retention and contributes to the rise of fungi. It is also advisable to ensure that feet are dry after swimming and allowed to air dry.
For some people an excess of anti-translational agents, such as 20% aluminum chloride (DRYSOL), helps reduce sweating. Treatment includes curing with topical antifungal creams, oral antifungal products, and powders. These include clotrimazole, luriconazole, and sertaconazole cream. Oral capsules will include grisefulvine, itraconazole, ketoconazole, and ciclopirox. Ketoconazole zing remains available; Clotrimazol Powder is still available in this region.
Topical steroid creams are contraindicated. They have every opportunity to aggravate infection and lower the body’s defenses against penetrating fungal organisms. They are used primarily to cure non-infectious causes. of athlete ’s foot.
Treatment should take at least one month and one week after disappearance of visible lesions of the disease to prevent repetition of latent disease.
Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
Athletes foot is a contagious fungal infection that causes all kinds of itchy skin problems on your feet. Itchy, hot, burning rash on infected skin. Treating athletes foot allows the fungus to spread further and cannot disappear.
Verdict.
What is athlete ’s foot?
Athlete’s foot is considered a fungal joint infection (caused by a fungus). Athlete’s foot causes an itchy, burning rash on the skin of one or both feet. Athlete’s foot between the toes is even more problematic, but can also affect the feet, soles, and heels. Your skin may peel off and crack or develop a glans. Sometimes your feet will smell dirty.
Athlete’s foot is a form of ringworm; Tinea Pedis is another name. for athlete Tinea is another name for ringworm and pedis means feet or legs.
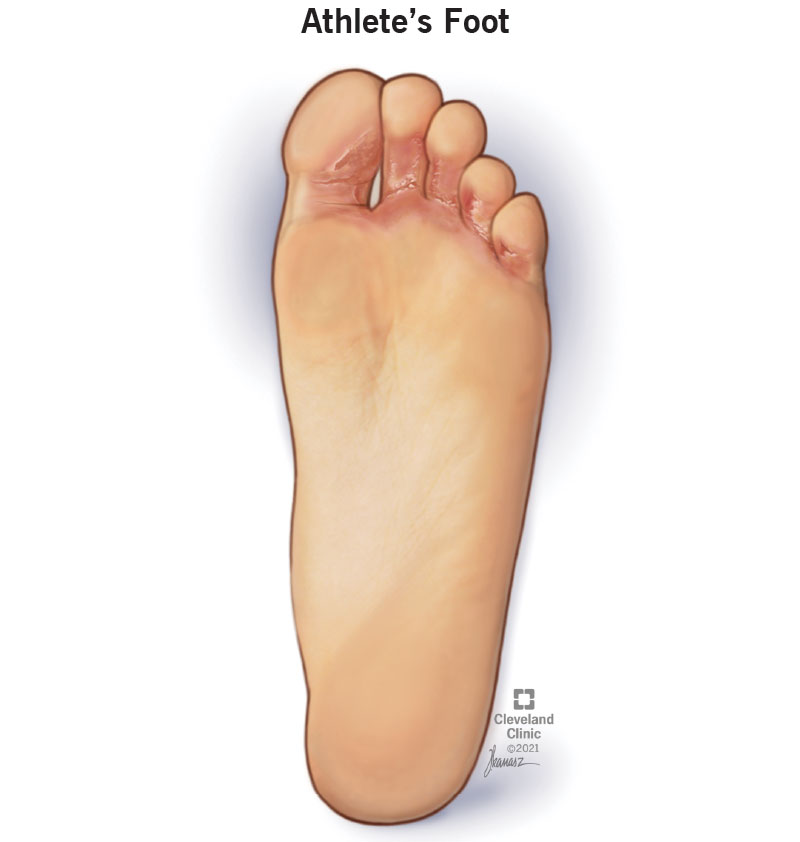
What does athlete ’s foot look like?
Athlete’s foot can affect the skin between the toes, bottoms of the feet, elbows of the feet, edges of the feet, and heels. Your skin may look irritated (red, purple, gray, or white), flaky or woven.
Who is at risk?
Everyone suffers from athlete’s foot. In particular, it is most common in men (and those assigned male at birth) and those over the age of 60. They are more likely to develop athlete ’s foot if you have:
- Diabetes.
- Obesity.
- Weakened immune system.
- Injury or damage to foot tissue.
How common is athlete ’s foot?
Athletes’ feet are omnipresent. Estimates suggest that between 3% and 15% of the population has has athlete feet, and 70% of the population will be one athlete indicator at a given moment in their lives.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of athlete ’s foot?
Symptoms of athlete ’s foot include:
- Cracked and peeling skin.
- Itchy skin.
- Skin rashes.
- Burning feelings.
What kind of athlete ’s foot?
Your sign is based on the type of athlete feet you have.
- Web Infection: web infection of the feet is considered the most common form of of athlete Foot. It usually touches the skin between the fourth toe (ring) and the fifth toe (little toe). Your skin can change color, crack, peel, or flake.
- Moccasin-like infection: Moccasin-like infections affect the bottom of your feet, heels, and the edges of your feet. Your feet may be painful for several days. The skin on the bottom of the foot will then thicken and rupture. Rarely, your toenails may become infected. There is a good chance that they will thicken, break down in small pieces, and fail.
- Vesicular tubercle infection: vesicular tubercle infections usually affect the bottom of the foot, but can occur anywhere on the foot. Raised or fluid-filled blisters (bubbles) form blisters.
- Ulcerated bedsores: ulcerated bedsores are the most uncommon form. of athlete Legs. Open ulcers (ulcers) are often found between the toes. Open ulcers are more likely to appear on the bottom of the foot.
What causes athlete ’s foot?
They can be caused by various types of fungus athlete ’s foot.
It is usually spread by skin contact or contact with skin flakes. It is spread in spaces used by large numbers of people, such as locker rooms, swimming pools, and saunas.
It can spread through contact with infected surfaces. You can. get athlete Share clean towels, socks, and shoes with someone who has athlete’s foot and step into the room. has athlete ’s foot.
Is athlete ’s foot contagious?
Athlete’s foot is contagious. It is a fungus that grows on or over your skin. Fungi (multiple configurations of fungi) need warm temperatures and moisture. People often wear socks or narrow shoes that keep their feet warm and wet. This is the perfect environment for athlete ’s foot to grow.
Diagnosis and Testing
How is athlete ’s foot diagnosed?
Your care provider can usually make a diagnosis as follows athlete Examine the feet and symptoms and step into the room.
Which tests are performed to make the diagnosis? athlete ’s foot?
In some cases, your caregiver can send a small skin (biopsy) and have it tested in the lab. A few drops of potassium hydroxide solution (KOH) will dissolve the skin cells so that only fungal cells are visible.
Treatment
How do I treat athlete ’s foot?
Antifungal cream, ointment, gel, spray or powder by prescription or freely available treatment athlete Foot. These products include clotrimazole, miconazole, tropical velocity, or terbinafine.
Some prescribed antifungal for athlete Tablets for feet. These tablets contain fluconazole, itraconazole, or terbinafine.
It is important to graduate in the absolute direction of the medication. If you stop very quickly, you have athlete come back and add the possibility of more difficult treatment.
How do I manage my athlete ’s foot symptoms?
Keep feet dry, clean and cool. Do not wear socks or shoes if possible. Beware of scratching your feet. Scratching your feet allows the fungus to spread to other parts of your body.
Will I feel better shortly after healing?
With proper diagnosis and treatment. athlete feet will disappear after one to eight months. Follow your doctor’s instructions.
It is important to follow the absolute direction of medicine. In the first stages of healing, the itching and complaints will disappear. When your signs disappear, you can still have it on your athlete feet. If you are not fully medicated, you athlete feet may come back and become more difficult.
What will happen if athlete Are your feet not treated?
Athlete’s feet can spread to the bottom of the foot. It is a moccasin athlete Feet. We step into the foot with moccasins. athlete Feet, the skin on the bottom, the heels and edges of the feet are dry, itchy and flaky.
In severe cases of athlete Feet, you can develop fluid-filled blisters or open ulcers. Blisters often occur on foot day, but can occur anywhere on your feet. Often open ulcers can be seen between the toes, but they have a good chance to develop on your feet. Your feet still have the opportunity to wear.
An athlete’s foot usually does not pass on its own. If untreated, there is an opportunity for it to spread to other parts of your body, including your …
- Nails: Fungal infections of the nails are most likely to be more difficult to treat. Often, they are more resistant to almost any treatment.
- Hands: Similar fungal infections can also spread to the hands. This occurs when an infected foot is injured or the same clean towel is used to dry the infected foot or hand.
- de Lies: what is the fungus that causes this? athlete Athletes feet can still spread to your gro radius. This condition is called jock itch. Fungus usually spreads from the feet to the gro radius after swimming or bathing and drying off with a clean towel.