Many readers are interested in the right subject: what does skin cancer look like? Our manufacturer is pleased to have already researched current studies on this fascinating subject. We will provide a wide range of answers based on the latest medical reports, advanced research papers, and sample survey information. Keep repeating to find out more.
Skin cancer It occurs when skin cells mutate and become unmanageable. In the skin cancer isn’t treated, the cancer It can spread to other tissues in the body, including bones and lymph nodes. Skin cancer Probably the most well-known type of cancer In the United States. One in five people in the United States at a particular moment in their lives have skin cancer, such as the Skin Cancer Foundation. There are many different types of skin cancer. cancer And it may not be easy to distinguish them from one another. This article describes the different skin types. cancer with pictures.
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like?
Many kinds of skin cancer It exists. Everyone looks a little different to the naked eye. A good rule to determine if a robot is considered robotic is the ABCDE rule.
Below you can see some of the different skin types. cancers You can see that Due to the fact that all skin cancer Otherwise, you will need to show an image of the bumps, well, lumps, or painful areas by a physician or dermatologist to be sure that the lesion is not considered a skin type. cancer .
1-Actinic keratoconus.
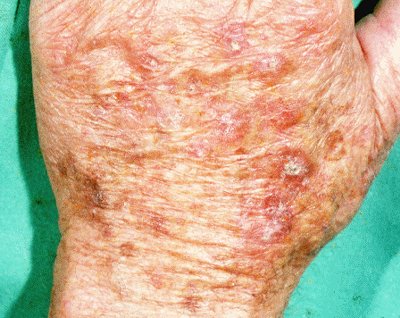
These are flaky and dry patches that usually occur on the face, head, neck, arms, and back. They are. not cancer However, the location in the forebrain where they are most likely to turn into cancer. cancer If they remain untreated. Most people with actinic keratoconus have fairly light skin and get them after years of sun exposure. They often occur in persons over the age of 40. It is advisable to treat them as they are more likely to turn into squamous cells cancer If they are not removed.
2. basal cell carcinoma
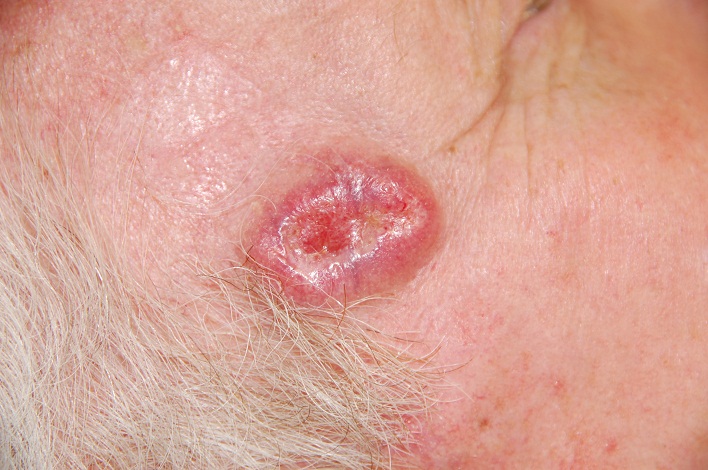
Basal cell cancer It is the most well-known skin cancer cancer That you can have. Like skin. cancer If you have this skin. cancer ? It usually occurs in light-skinned people, but can also occur in dark-skinned people. They have a chance to become ridges or skin that looks pearly, flesh-like, and contains iridescent dyes. Base. cancer Years of sun exposure or in tanning beds. They are most common in the neck, arms, and head, but are also most common on the stomach, legs, and chest. Until they spread, basal cells can cancer disseminate, basal cells can spread to adjacent material and convert to bone and nerves, actually leading to debridement and tissue damage.
3. pavement cell carcinoma
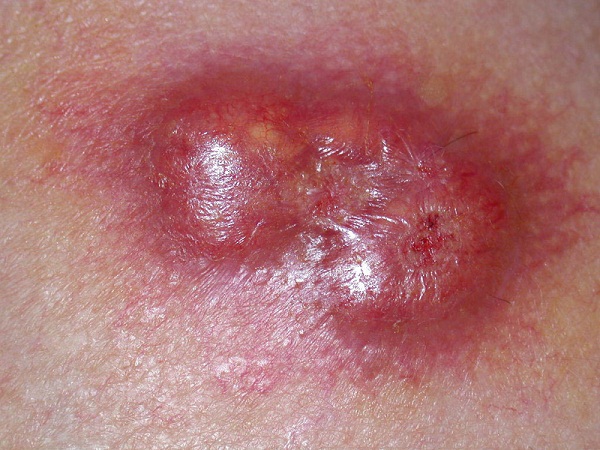
Squamous cell cancer Two common skin patterns cancer Polemiedesze is most common in light-skinned individuals, but in those who have dark skin a loss may be seen. They look like flaky areas, skin lesions that do not want to heal, or certain charlatanroad ridges on the surface of the skin. Pavement Cells cancer Usually on skin often exposed to the sun, especially outdoor ears, neck, character, bust, arms, hands, and back.Laesies often grow deep into the fabric if left untreated and likely to seed. This can lead to deformities in this area and should be treated as soon as possible after diagnosis.
4. melanoma
What does skin cancer Does it look like a melanoma? Melanoma is not as common as almost all other skin conditions. cancer However, it is very unsafe. It is associated with about 75% of all skin deaths. cancer It develops in skin cells, forms pigmented areas of the skin, and has the following characteristics
- Asymmetrical
- Irregular edges
- Variation in skin color
- Vastly crossed sections than normal birthmarks
- Evolution of volume and form
There are four common types of melanomas from the skin. cancer As can be seen in the close-up illustration, each type looks slightly different.
- Lentigo Maligna Melanoma. This type of melanoma includes flat, giant, and brown oaths usually seen in older patients.
- Superficial Diffuse Melanoma. This is a very diffuse melanoma. It is an irregular lesion of different color coffee and darker color. It can occur in people of any age.
- Acral Lelnigieus melanoma. This is not common. It occurs under the fingernails and toenails or on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands.
- Uvul Melanoma. This can have numerous colors, including red, dark, and blue. It can also be transparent. It usually occurs when there are more exposed areas on the skin exposed to the sun.
5. sarcoma of Kaposi
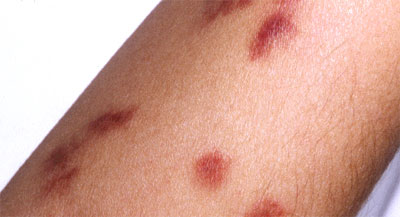
Now you are imagining it: “What does the skin look like? cancer Outside? ‘ You still owe it to Kaposis sarcoma to focus your care on it. Technically, it’s not an image of the skin. cancer , but it is a cancer It happens on the skin, especially the legs and feet. It affects the cells lining the blood vessels near the skin, causing brown to reddish skin ulcers. It does. a cancer This has its own basis in the herpes virus. It is usually seen in AIDS patients.
How to Diagnose Skin Cancer
Determining Skin Cancer. cancer Can your doctor do everything right?
- Examine the skin. The physician can thoroughly examine the skin to see if there are any non-reliable injuries that are likely to present themselves as skin. cancer . If unreliable lesions are identified, the physician may have to perform additional studies to diagnose the disease.
- Take a tissue biopsy. The physician removes a piece of skin to view it under a microscope. Suspected nurturing can be sent in whole or in part for tissue biopsy. Microscopic diagnosis is superior to seeing what the skin is preparing. cancer See it with the naked eye.
After diagnosis, one can try to recognize possible ways to cure the skin. cancer In the meantime, please watch the video below. In the meantime, watch the video below.
Are you at risk for skin cancer?
Now you can see what “your skin looks cancer ” look like. You may want to know how it happens and how your risk increases.
The genesis of skin cancer These are mutations of DNA in the cells, elements of the skin. These mutations lead to an uncontrolled increase in skin cells. Certain things will ensure that you run more risks:
- Light-colored skin. Skin cancer Can occur in people of all skin colors, but those with more pigment in their skin are more likely to be protected from the sun’s UV rays. If you have freckles, blue eyes, blonde or reddish hair, or only burn, you are more likely to develop skin diseases. cancer Compared to people with darker skin.
- Sunburn History. If you burned at least once when you were young, you are at a higher risk for skin infections cancer As you get older. As an adult, do not try to burn.
- Too much sun exposure. Spending a lot of time in the sun increases your chances of developing skin diseases. cancer Especially if you do not cover your skin with clothing or sunscreen. Sunbeds also increase the risk of skin infections. cancer .
- Sun ammunition. If you live in a warm, sunny climate, you have a greater chance of sun exposure and skin damage. cancer The same is true if you stay close to the sun. The same applies to higher climates where you stay closer to the sun.
- Positive history. If you have a brother, sister, or caregiver with skin disease, your risk of getting the disease is greater. cancer You run a higher risk of getting the disease.
- Poor immune system. If your immune system is weak, you will not fight. off cancer You also run a higher risk of skin infections. cancer People with HIV, AIDS, or taking immunosuppressive drugs are at higher risk.
- Exposure to radiation. People who have received radiotherapy for skin problems, such as acne or eczema, have an increased chance of skin disease. cancer .






